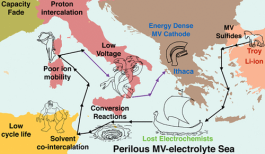
Abstract
The rapidly expanding field of nonaqueous multivalent intercalation batteries offers a promising way to overcome safety, cost, and energy density limitations of state-of-the-art Li-ion battery technology. We present a critical and rigorous analysis of the increasing volume of multivalent battery research, focusing on a wide range of intercalation cathode materials and the mechanisms of multivalent ion insertion and migration within those frameworks. The present analysis covers a wide variety of material chemistries, including chalcogenides, oxides, and polyanions, highlighting merits and challenges of each class of materials as multivalent cathodes. The review underscores the overlap of experiments and theory, ranging from charting the design metrics useful for developing the next generation of MV-cathodes to targeted in-depth studies rationalizing complex experimental results. On the basis of our critical review of the literature, we provide suggestions for future multivalent cathode studies, including a strong emphasis on the unambiguous characterization of the intercalation mechanisms.