Abstract
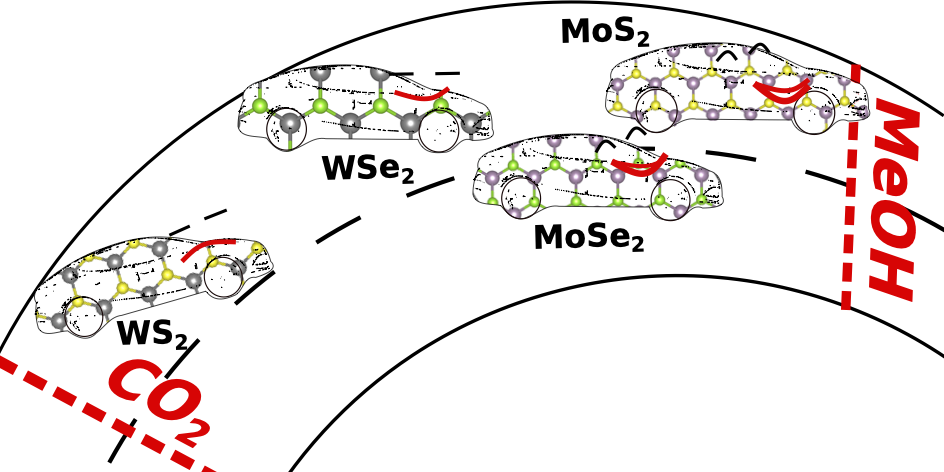
We computationally investigate the catalytic potential of MoSe2, WS2, and WSe2 nanoribbons and nanosheets for the partial hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol by comparing their electronic, adsorption, and defect properties to MoS2, a known thermo-catalyst. We identify Se-deficient MoSe2 (followed by WSe2) nanosheets to be favorable for selective methanol formation.